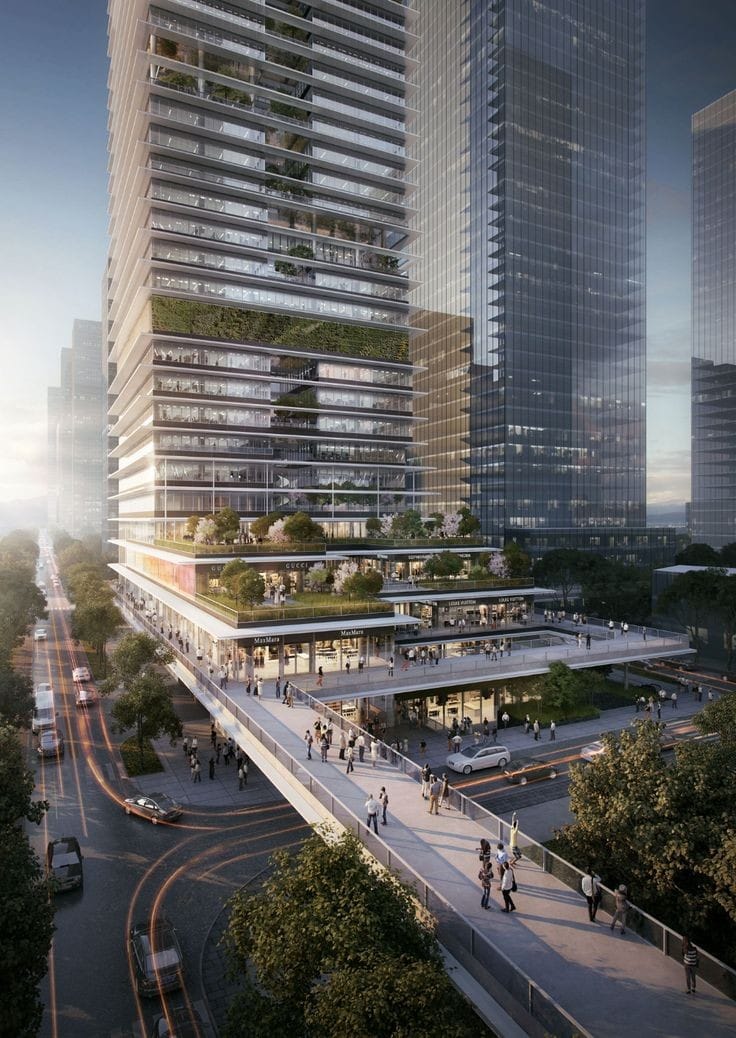
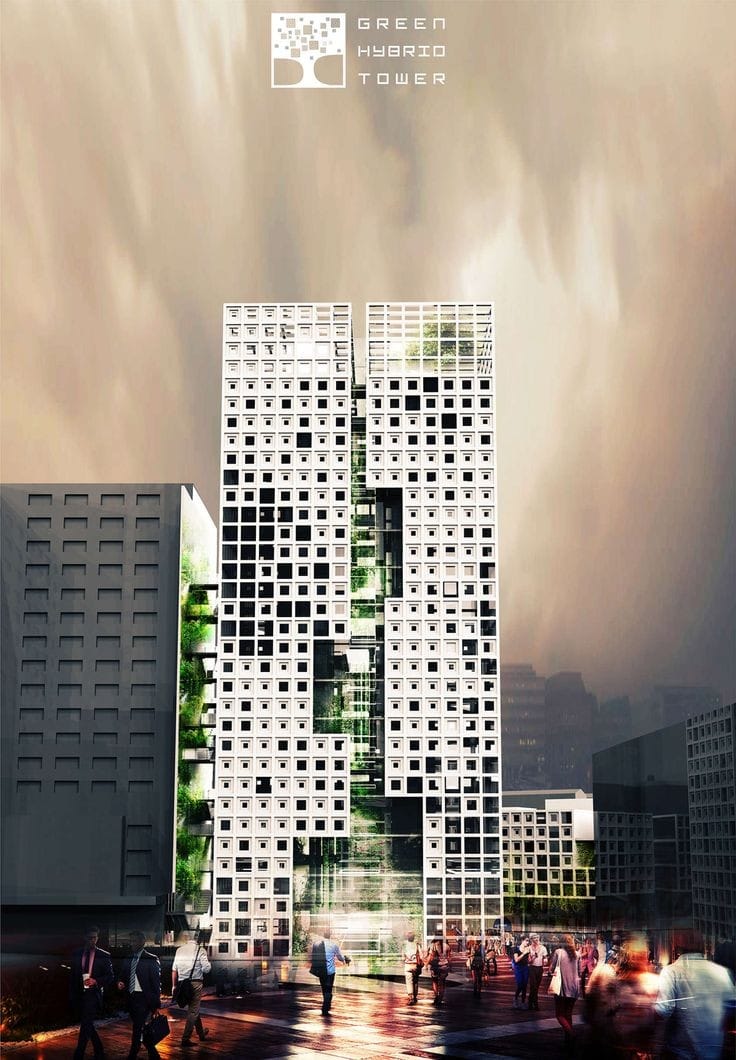
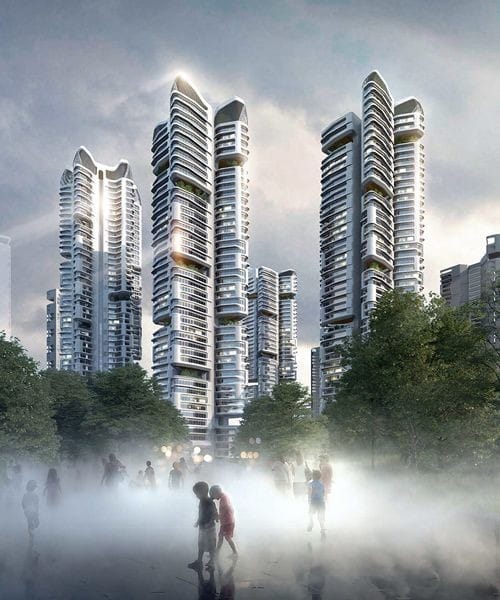
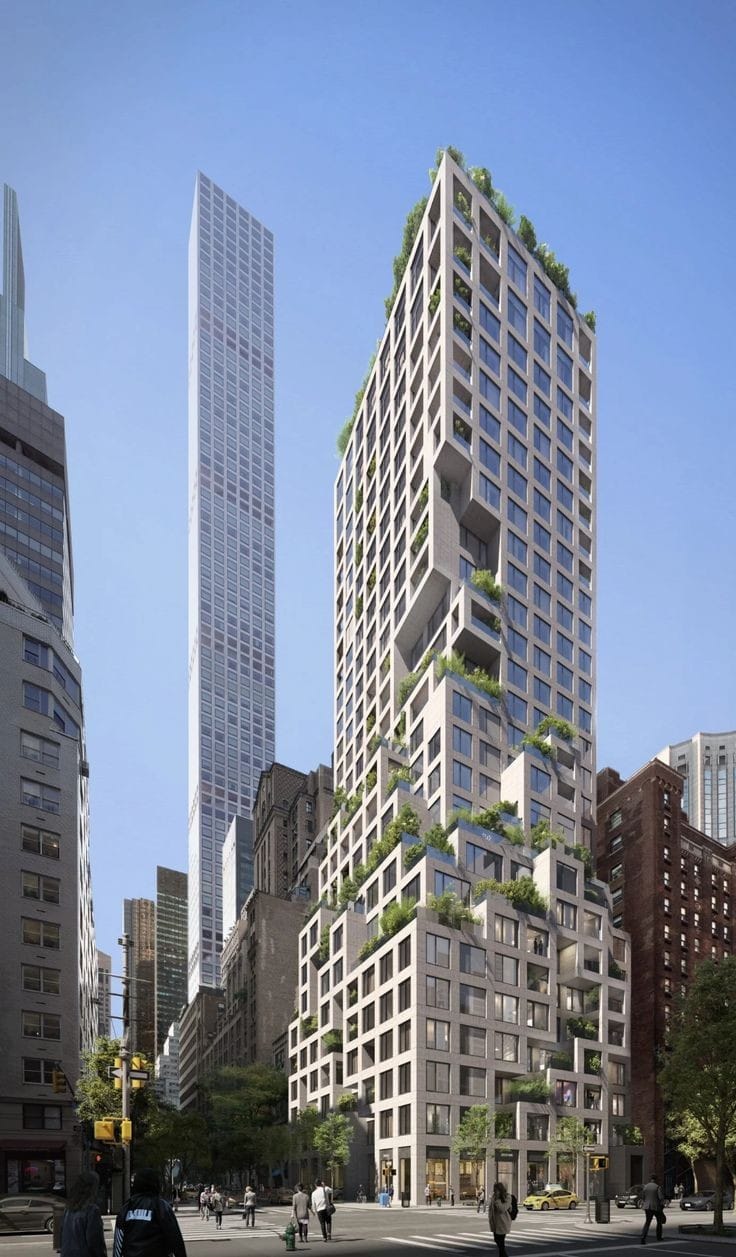
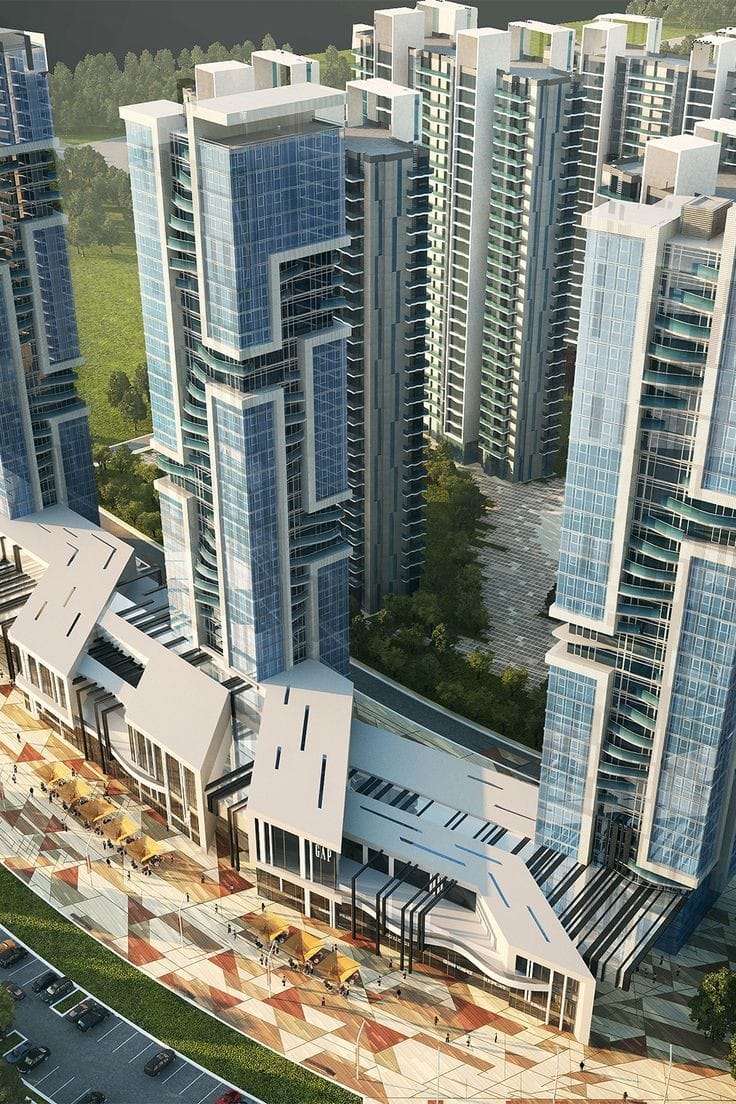
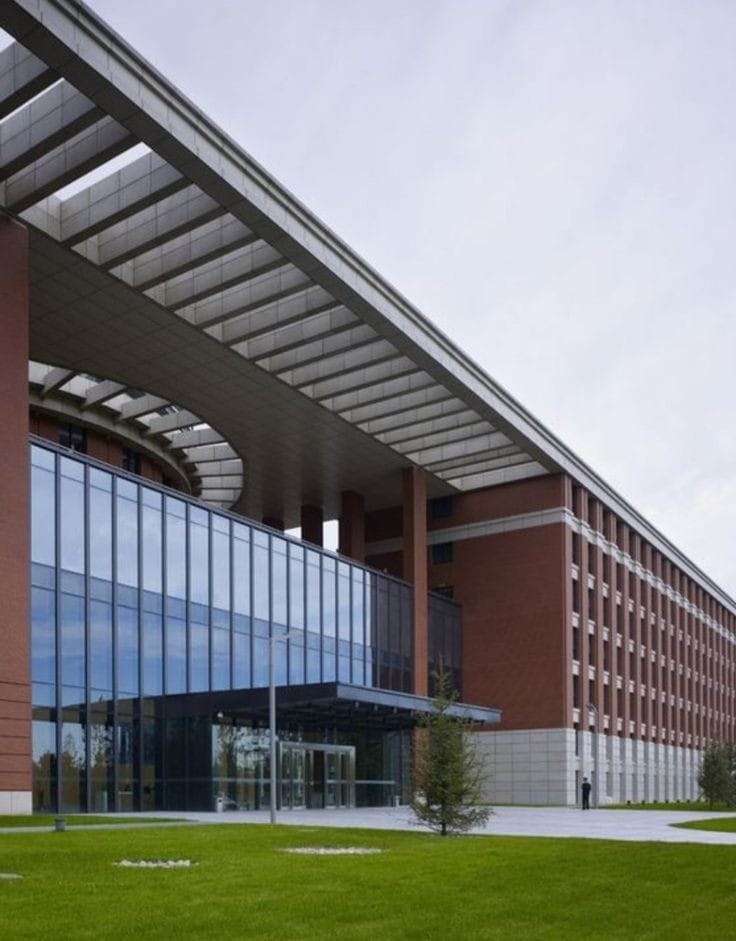
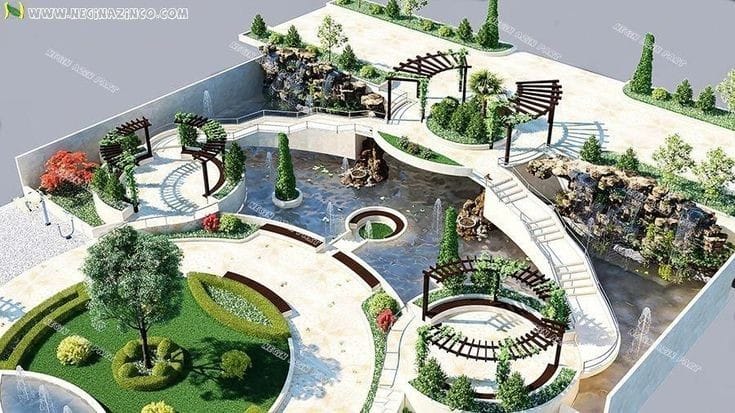
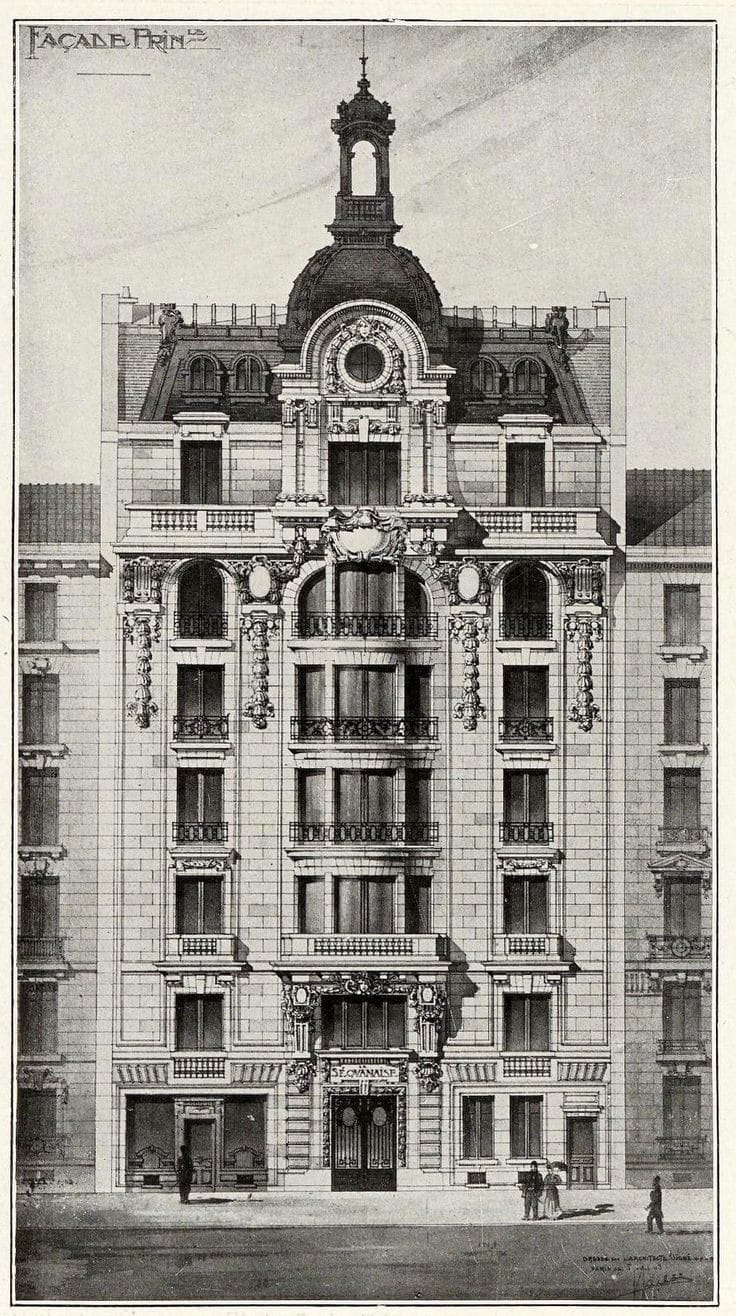
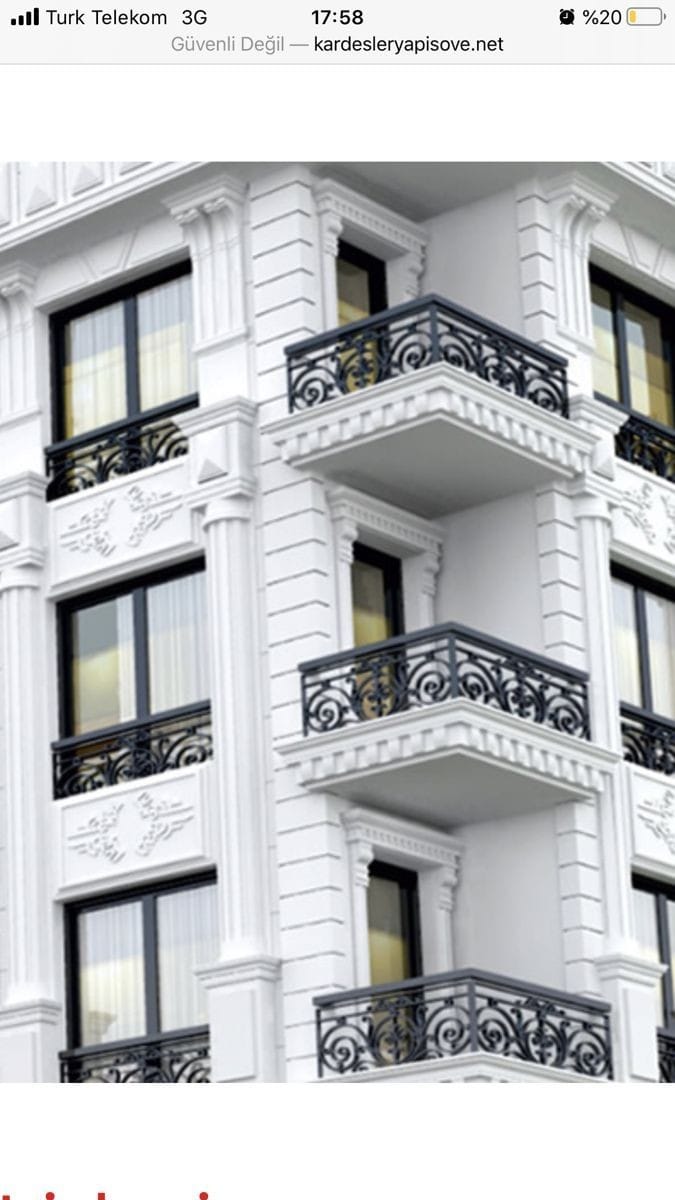
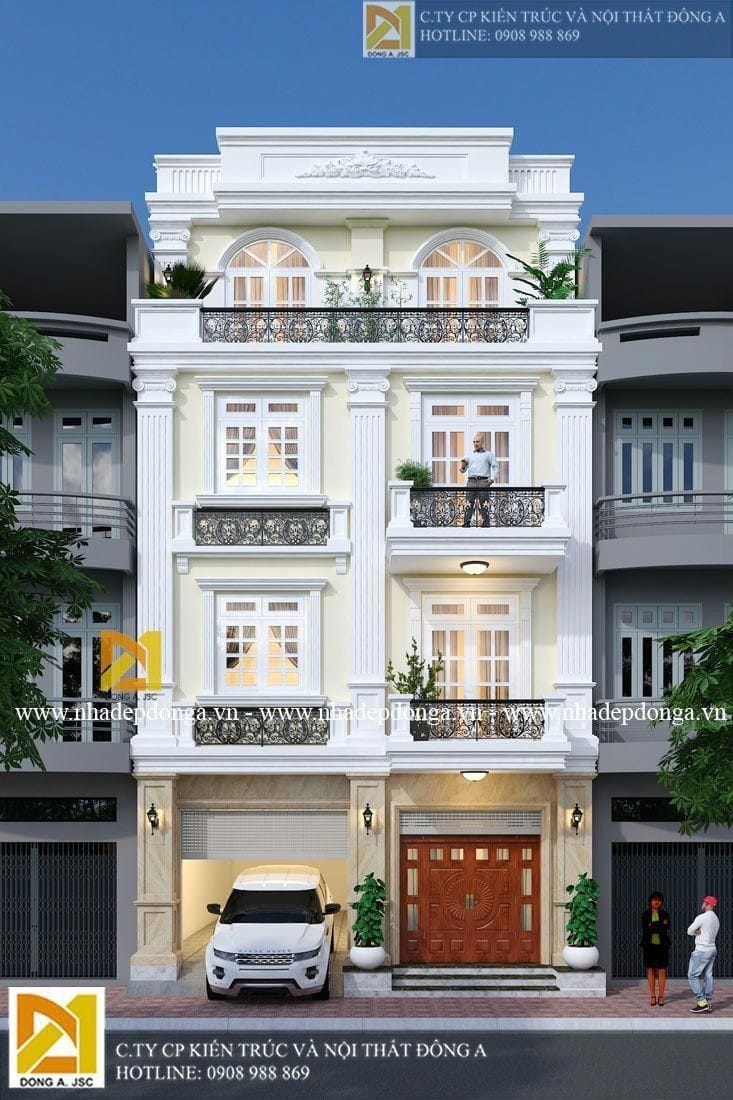
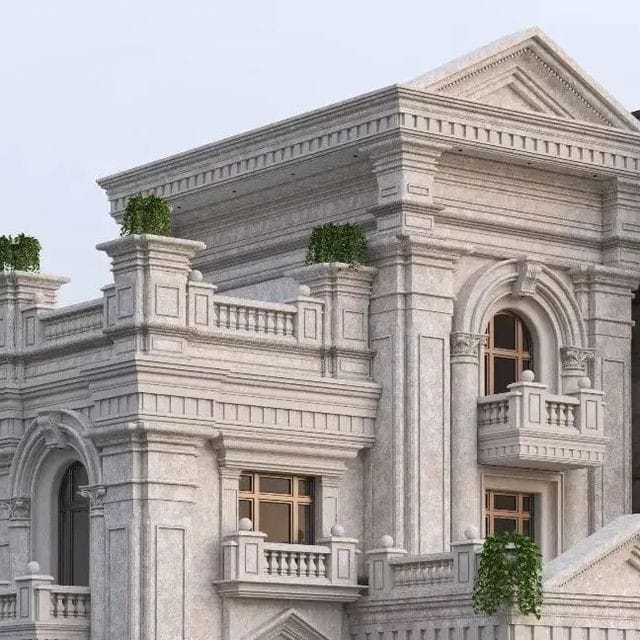
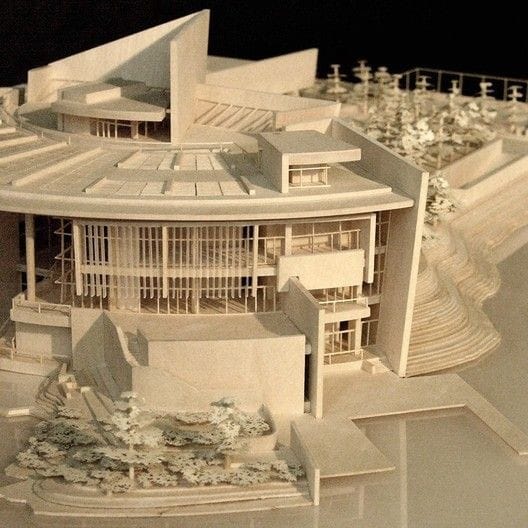
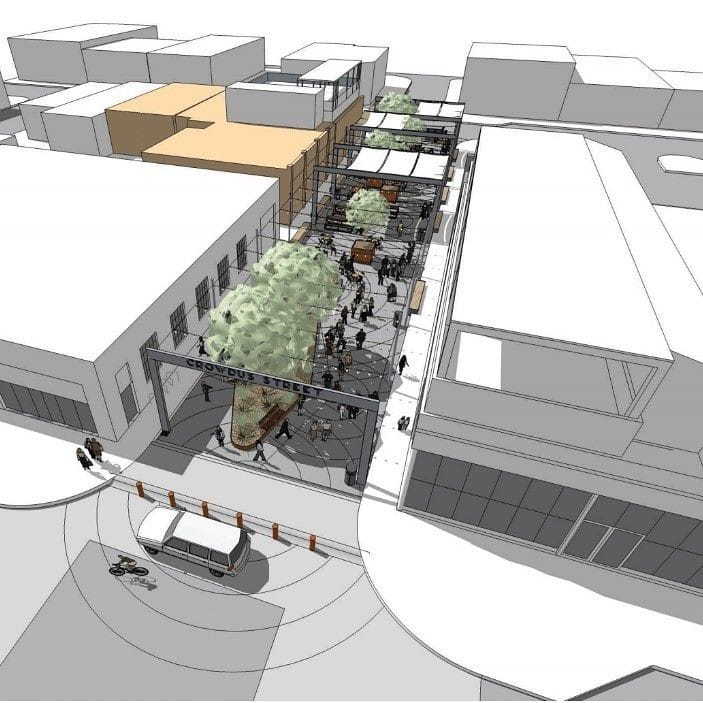
About us
Vision:
Change and mould the world for a better living space, Design better living standards for the people. Architectures,ecological system Conserve and preserve natural resources, heritage architecture forests and all that deserves to be conserved. designs of tomorrow, for future.With care, love and diligence Team of professionals in the design arena engineering field and management area collaborative, coercive, conclusive Thought are asserts and strength of our team.
Shall uphold the public aspirations, dignity, respect, pluralism to the best of our ability and general standard under the terms and conditions laid down of the institutions of architects, engineer,designers, management professionals.
Take moral responsibility ensuring the quality of projects under taken, in terms of designs, contracts, tenders, materials, and time schedules execution of projects.
Objective:
Great thought can shape peoples future great homes Comfort good living environment so is clustered homes shall bring in social justice in life style of families together greenery can soothe, children’s desires of being at positiveness.
To highlight public awareness on fundamentals of architecture, urban design and finest forms of design our team’s objective is to strive hard to meet public demands of apathy algorithm of architecture.
Modern architecture is absolute design of liberalism, idealism, pluralism and perfectionism. Architecture is forms of systematically analysed artistic impressions of creative thoughts to represent public life style. Illusions are drawn to practical applications of life.
Imaginations are tabled and labelled to conclusion of engineering subjects turning designs more colourful than ever.
A new version of architecture style is fast emerging in the midst of public outcry of perfectionism in designs.
Technological innovations shall reshape these versions of architecture neo architecture futurism shall anchor and shoulder the responsibility of creating futurism in architecture supported by scientific evolutions.
Maisonette Group
• Architecture • Interior design • Landscape design • Town planning • Project management • Electrical engineering • Mechanical engineering • Civil engineering Architecture : the art and technique of designing and building distinguished from the skills associated with construction. To enhance, articulate design fundamentals to the best of general merits, Presentation drawings, sketches, three dimensional drawings.
Styles of architecture
• Classical architecture • Tudor architecture • Neoclassical architecture • Cape cod architecture • Italian architecture • Indian architecture • Greek revival architecture • Victorian architecture • Arts and crafts architecture • Renaissance architecture • Contemporary architecture • Brutalist architecture • Modern architecture • Post modern architecture
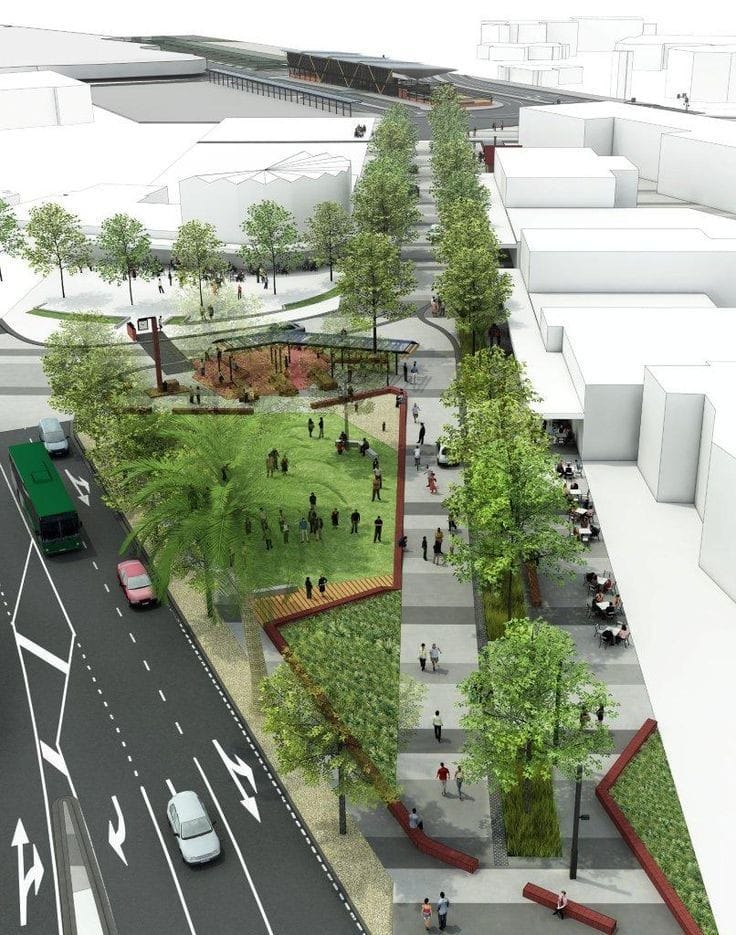
Town planning
Principles of Town Planning
Town planning cannot be studied in isolation. It involves the study of various subjects such as engineering, architecture, surveying, transportation planning etc. The intention of the town planning is to satisfy the needs of our future generations and prevent the haphazard growth of the town. Some of the guiding principles of town planning are as follows.
1. Zoning
The town should be divided into suitable zones such as commercial zone, industrial zone, residential zone, etc. and suitable rules and regulations should be formed for the development of each zone.
2. Green Belt
Green belt is non-development zone on the periphery of the town. It prevents the haphazard sprawl of the town restricting its size. In essence, a green belt is an invisible line designating a border around a certain area, preventing development of the area and allowing wildlife to return and be established. Greenways and green wedges have a linear character and may run across the town and not around the town.
3. Housing
Housing has to be carefully studied and designed to suit the local population. Care should be taken to see that there is no development of slums since it would be responsible for degrading the life of the citizens. There are various types of housing styles. When a landuse plan is made, zones for independent housing, midrise buildings, high rise buildings are allocated.
4. Public Buildings
Public buildings should be well grouped and distributed throughout the town. Unnecessary concentration of public buildings should be avoided. Factors such as parking facilities, road widths have to be taken into consideration while allocating the space for public buildings.
5. Recreation Centres
Recreation centres have to be given importance while designing a town. They are necessary for the recreational activities of the general public. They include parks for walking and cycling, amusement parks etc.
6. Road Systems
Road network hierarchy is very important. The efficiency of any town is measured by the layout of its roads. A nicely designed road system puts a great impression in the minds of people, especially the visitors to the town. The provision of a faulty road system in the initial stages of town formation proves to be too difficult and costly to repair or to re-arrange in future.
7. Transport Facilities
The town should be provided with suitable transport facilities so that there is minimum loss of time from place of work to the place of residence. Efficiency in transport facilities includes both public and private networks. Public transportation network includes access to buses, trains, trams and trolleybuses. Efficiency in using the public transport will determine the success of that town in terms of design.
Objectives of town planning
Health
Sophisticated beauty Connective sense with culture and environment
Convenience
Zoning
Green belts
Road network
Mobility solutions
Principles of town planning and design
Identity
Connectivity
Urban integration
Suitability
Amenity
Vibrancy
Safety
Environment
Duplicate models of the project in detail, Plans of the project in detail, shall present architecture at the best of merits and quality, innovative designs are our principles of thoughts in reshaping the future.
Public has different views of expectations on their life style requirements, where building designs are concerned.
Presentation skills can meet their demands and expectations of architecture.
Architecture design shall be authentically plea ring, appealing, relaying to the eyes of the public.
Interior design
In classified sub version of architecture so as to design interior spaces the best.
This includes interior space planning and analysis of movements horizontally and vertically.
Lighting natural and electrical is part of interior design, so is ventilation, ducting and exhaust system.
Good interiors could be designed while buildings are being Designed, then forming the comprehensive architectural concepts.
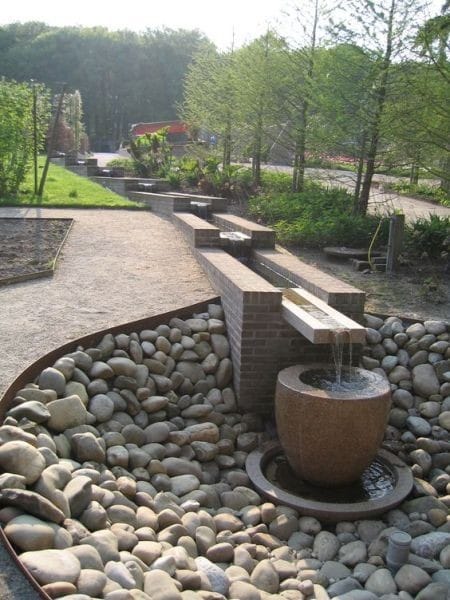
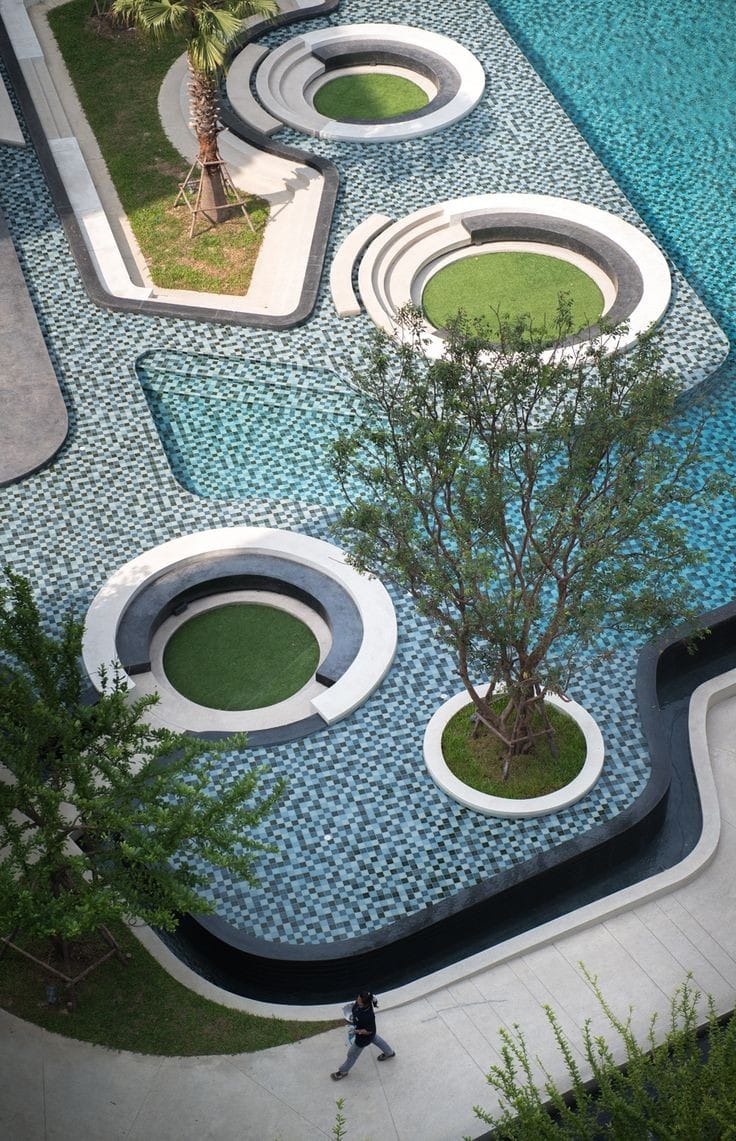
Landscape design
Is a specialized architectural subject mainly one doors, Can add additional beauty to the building architecture unity.
Balance
Proportion
Transition
Unity in the effective use of elements in design to convey a theme, Unity is achieved by implementing a design consistently over a landscape trough mass planning or repetition, where as balance is a term of comparison between two segments of a landscape, unity pertain to the overall picture of a landscape, unity has been achieved when the viewer senses that all the individual elements of landscape, further fit together to form a coherent theme.
Proportion in the sense or requirement that the size of the individual components or groups of components in a landscape fit in to the whole landscape, harmoniously one way to achieves proportion is trough proper use of transition, applied to the size of the respective components.
Transition is the gradual charge, achieved by the manipulation of the basic elements of colour, scale, line form, texture
PlatformPlat texture
Line
Colour theory
Focal point
Project management
Project is a unique endeavour, under taken to achieve planned objectives, which could be detailed in terms of outputs, outcomes benefits.
A project is usually deemed to be success if it achieves the objectives according to their acceptance criteria, with in an agreed time scale and budget time, cost and quality are the building blocks of every project.
Time: scheduling in a collection of technique used to development present schedules that show when work will be performed.
Cost: how are necessary funds required and finances managed?
Quality: how will fitness for purpose of the deliverables and management processes are assured.
Projects are separate from business as usual activities and occur when an organization wants to deliver of solution to set requirements within an agreed budget and time frame.
Project require a team of people to come tighter temporarily to uses on specific project objectives as a result effective team work is central to successful projects.
Scale, Significance, Complexity, Objectives, Out puts, Outcomes, Strategic objectives, Initiation, Planning, Control
Electrical engineering
o Designing electrical systems
o Residential projects
o Commercial projects
o Industrial projects
o Directing electrical contractors
o Resolving electrical issues
o Developing cost estimate
o Managing constructions schedules
o Conduct of system testing
Mechanical engineering (in building industry)
o HVAC design
o Healing, ventilation and air condition plumbing design.
o Fire protection
o Energy efficiency
Civil engineering
o Infrastructure engineering
o Structural engineering
o Environmental engineering
o Geotechnical engineering
o Transformation engineering
o Coastal engineering
o Water engineering
o Earth quick engineering
Structures
1. load bearing structures
2. thrush structures
3. frame structures
4. pre engineered structures
5. mass structures
6. tensile structures
7. composite structures
Karnataka architecture
We at maisonette Architects Company in Karnataka have comprehensively gone through the historical growth of architecture and study of history of Karnataka architecture. Has added a additional knowledge in designing present day projects.
Architecture of Karnataka (345 to present)Type Period
Kadamba architecture – synthesis of several schools (345 to 525)
Dravidian architecture (Western Ganga Dynasty) (350 to 550)
Badami Chalukya architecture or the Vesara style (543 to 753)
Dravidian & Rekhanagara architecture of Rashtrakutas (753 to 973)
Western Chalukya architecture (Kalyani Chalukyas) (1000 and 1200)
Hoysala architecture of the Hoysala Empire (1100 and 1400)
Vijayanagara architecture of the Vijayanagar Empire (1336 to 1648)
Indo-Islamic architecture of the Deccan Sultanates (1490 to 1686)
Keladi Nayaka architecture of the Nayaka kingdoms (1499 – 1763)
Architecture of Kingdom of Mysore – Blends of Hindu, Indo-Islamic, Rajput, and Gothic styles of architecture (1399 to 1947)
Indo-Sarcenic and Muslim architecture of Tippu Sultan (1780)
Buddhist Viharas, Tibetan Culture & Tibetan architecture at Bylakuppe (1953 to present)
Sikh architecture of Bidar & Bangalore (1512 to present)
Neo-Gothic church architecture (1933 to 1956)
Neo-Dravidian architecture (1947 to present)
• Kadamba architecture.
• Dravidian architecture.
• Badami Chalukya architecture.
• Dravidian and Rekhanagara style of architecture of Rashtrakutas.
• Western Chalukya architecture.
• Hoysala architecture.
• Vijayanagara architecture.
• Indo-Islamic architecture
Karnataka is the State that is known for showcasing some of the finest examples of Islamic, Hindu, Jain, and Colonial architecture.
The State has been ruled by some of the most powerful empires in the Indian history, from the Cholas, Chalukyas, Hoysalas, to Vijayanagar Empire, and each of them has left their own imprints in the monuments and temples that they built.
The magnificent temples and structures that they built thousands of years ago stand tall as majestically as ever till today, reminding generations about the rich architectural heritage of the country. Here’s a brief overview of the seven amazing buildings from the Karnataka architecture which stand out due to their architectural brilliance....
Architecturecomes from Latin word architectura from Greek word ‘architecton’
‘Archie’ meaning chief and tecton meaning builder it can also meant the physical structure of buildings the study of science and art of designing buildings and also structures that are not of buildings.
Architecture is not just about the design and construction of a building, but also the space and ambiance of the structure. It also considers the social and environmental impacts of a building. Aside from this, it also includes the practical aspects of the construction of a building, such as scheduling, budget, administration, and the documentation which are usually drawings which show the plans and specifications of the technical side of the project, and also other systems that will be constructed together with the building.
According to Marcus Virtruvius Pollio, a Roman architect in his “De Architectura” (English: On Architecture), the oldest surviving written work on architecture from the 1st century AD, a good building satisfies three principles: firmitas, or the durability and robustness of a building; utilitas, the suitability for the purpose it is built for; and venustas, or beauty, meaning the building should be pleasing to the eyes. It is the first book that tackled architectural theories and style such as those of the Greeks and the Romans.
American architect Louis Henry Sullivan proposed a concept and coined a phrase for architectural design, “form follows function,” which means that the shape of a building should be based on its supposed function. While this concept not only applies to buildings, it has always been wrongly credited to American sculptor Horatio Grenough.
Kinds of Architecture
There are many types and styles of architecture.
Building is actually a craft and first started out as using whatever materials were available. Architecture is a more formal and respectable kind of craft. In ancient civilizations, their architecture is associated with the supernatural and the divine, and at times a symbolic representation of the current ruler, the elite, or the state.
The Greek and the Roman styles of architecture took inspiration and evolved from civic ideals rather than religious ones. In Asia, some of the writings on architecture are Kao Gong Ji (Record of Trades) which was published by one Lin Xiyi in 1235, Shilpa Shastras (Arts and Crafts) from Ancient India, and Manjusri Vasthu Vidya Sastra of Sri Lanka, which is a manuscript describing the construction of the Buddhist monasteries of Sri Lanka. Islamic architecture, like ancient civilizations, molded their architecture around their religious needs but also considered the needs of the society. In Europe, the major buildings during the middle ages were the abbeys and cathedrals. Merchants, tradesmen, and clerics who travelled spread architectural knowledge throughout Europe which resulted in the Romanesque and Gothic styles. Classical learning was revived in the 1400s in Renaissance Europe where specific architects such as Brunelleschi and Michelangelo thrived. In the industrial age, the discovery of new materials and technology and the introduction of mass production, began to separate architecture and engineering, paving the way to the cheaper construction of buildings. It was also when architecture began to focus on aesthetics such as beautiful drawings.Modern architecture had an avant-garde tone since architects after World War I wanted a completely new style for the post-war times. With the modernization of society, architecture began to break away from the Virtuvian ideals. Postmodernist architecture came after World War II and its influences are still found today. This type of style allows designers to freely express their talent in diverse ways from forms of sculpture and ornaments to anthropomorphism.
Architecture will find a way to fit the needs of society and will even revive itself when society wants to see examples of history as they were in the day.
The Indian state of Karnataka is a fascinating region with a rich history that dates back thousands of years. The region has been home to many different cultures and civilizations, each of which has left its mark on the area. In this article, we will take a look at the ancient history of Karnataka and explore some of the most important historical events that have taken place in the region.
Architecture is not about the design and construction of a building.
A Brief Overview Of Ancient History of Karnataka
The region now known as Karnataka has been inhabited for millennia. The first settlers are thought to have arrived around 3000 BCE, and the region has been home to many different cultures and civilizations since then. The region has been ruled by the Mauryas, the Chalukyas, the Rashtrakutas, the Vijayanagar Empire, and the Hoysalas, among others. Each of these empires has left its mark on Karnataka in the form of art, architecture, and culture.
One of the most important periods in the history of Karnataka is the Chalukya dynasty, which ruled from the sixth to the twelfth century CE. The Chalukyas were responsible for some of the most impressive architecture in Karnataka, including the cave temples at Badami and Aihole. They were also responsible for the construction of many Hindu temples, including the Mahakuteshwara Temple and the Kailasa Temple.
The Vijayanagar Empire was another important empire in Karnataka’s history. The Vijayanagar Empire was founded in the fourteenth century CE, and it reached its height in the sixteenth century CE. The Vijayanagar Empire was responsible for some of the most impressive architecture in Karnataka, including the Vijayanagara Fort and the Virupaksha Temple.
The Hoysala Empire was another important empire in Karnataka’s history. The Hoysala Empire ruled from the eleventh to the thirteenth century CE. The Hoysalas were responsible for the construction of many Hindu temples, including the Chennakesava Temple and the Hoysaleswara Temple.
British Colonial Period In Karnataka
Karnataka has a long and varied history. The region was originally inhabited by hunter-gatherers but around 3000 BCE, the first farmers settled in the area. By 1000 BCE, iron-using settlers had arrived and by 500 BCE, there was a flourishing trade in gold and other metals. Around this time, the region was also home to the powerful kingdom of the Chalukyas.
In 1761, Hyder Ali, the ruler of Mysore, defeated the last of the Chalukya kings and took control of Karnataka. His son, Tipu Sultan continued his father’s work and by 1799, he had conquered much of southern India. However, in 1799, the British defeated Tipu Sultan and took control of Karnataka.
The British ruled Karnataka until 1947 when India gained independence. Since then, Karnataka has been an important part of the Indian Union.